At a glance
Natural resources are the foundation of Hawaiian culture, both past and present. KS has a long-standing commitment to steward these precious resources by protecting watersheds with native species, reestablishing fishponds, and managing water resources. By 2030, KS anticipates increasing acres of watershed under high-level protection on KS ‘āina by 65% in support of the Hawaiʻi’s 30 x 30 watershed target.
Over 51,000 acres of watershed on KS ʻāina are projected to be protected by 2025. Fencing projects such as Mauka Keawanui (Pāku‘i), Central ‘Ōpae‘ula, Waiawa, Lā‘au, and Nāmolokama fencing projects contribute to this target.
AA+ LF, NRM, SSC, GWE | UNSDG 11, 14, 15 | GRI 201, 203, 304 | AAEF 3.0, 6.0
Exploring Pauahi’s ‘āina
During the COVID-19 pandemic, KS recognized a growing need for more virtual resources and accessible community engagement. As a response, KS published interactive online maps, allowing users to explore Pauahi’s ‘āina.
The maps have detailed layers with information about all land in Hawaiʻi related to natural and cultural resources. Maps are searchable by KS agricultural land, KS conservation land, wetlands, county zoning, and more. Visit the maps here.
A+SSC, GWE | UNSDG 9, 11, 15 | GRI 413 | AAEF 5.0, 6.0
Conservation fences
Almost 40,000 acres of KS ‘āina are under high-level protection, or fenced to exclude all ungulates such as feral cattle, pigs, and goats. By 2023, the total acreage protected will increase by almost 9%.
Notable projects include sites such as:
- Keawanui, protecting 2,000 acres of Moloka‘i’s wet forest
- Nāmolokama and Lā‘au, protecting 1,650 acres of diverse native wet forest in Mauka Lumaha‘i
- ‘Ōpae‘ula, protecting 700 acres of diverse native wet forest in Mauka Kawailoa
- Waiawa, protecting 1,000 acres of native forest and shrubland in Mauka Waiawa
A+NRM | UNSDG 15 | GRI 201, 203, 304 | AAEF 5.0
Nearshore resources
In 2016, the State of Hawai‘i launched the Marine 30x30 Initiative which aims to effectively manage Hawai‘i’s nearshore waters with 30% established as marine management areas by 2030.
KS has made leveraged system investments to empower community marine stewardship efforts, increase public funding for ocean conservation, develop strategic communications around 30x30, as well as advance and aggregate the latest ecological marine science. Read more here.
A+SSC, NRM, GWE | UNSDG 13, 14, 15 | GRI 201, 203, 303, 304, 413 | AAEF 5.0
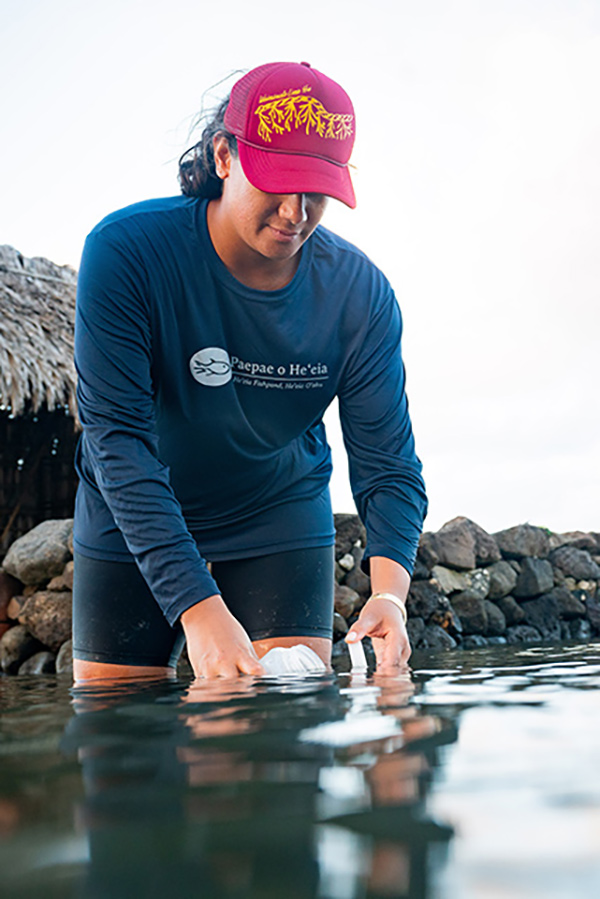
Fishpond management
KS is dedicated to the restoration and stewardship of fishponds, or loko i‘a, as living, productive, and sustainable ecosystems necessary to the perpetuation of Hawaiian culture and practices. These fishponds are important for future food security in addition to their other benefits as resilient water management systems.
KS fishponds managed by collaborators include Loko Ea Fishpond, He‘eia Fishpond, and Keawanui Fishpond. Wherever possible, KS students get involved with the management of fishponds to further their education in sustainable ecosystems and culture.
A+LF, NRM, SSC, GWE | UNSDG 11, 14, 15 | GRI 201, 203, 303, 304, 413 | AAEF 3.0, 5.0
Stormwater education
Kamehameha Schools collaborated in the beta test for the new app that became the Follow the Drop program, which aims to bridge the Hawai‘i Fresh Water Initiative goals into Hawai‘i’s classrooms and communities.
The overarching goal is to unite and lay the foundation of knowledge for Hawai‘i’s youth to develop critical thinking skills and solution-based opportunities to meet the state’s water security goals. Learn more about the Hawai’i Fresh Water Initiative here or the Follow the Drop program here.
A+NRM, SSC, GWE | UNSDG 4, 13, 14 | GRI 303, 404, 413 | AAEF 5.0